AI Summary
This AI-generated content is derived from the source article.
Analysis failed, AI robot malfun
方法的重载 #
好处 #
- 减少方法名称的记忆
- 可以忽略参数的自动类型转换
定义 #
方法的重载是指一个类中定义了多个相同名字的方法,需要每个方法具有不同的参数类型或者参数类型的相同个数不同,调用的时候可以根据该方法的参数类型或者个数类型区分对应的方法;方法的重载和返回值类型,修饰词没有关系
适用场景 #
当一个类中出现相同的功能时,但是需要的参数不同 参数 类型不同 个数不同
要求 #
- 必须在同一个类中
- 方法名的相同
- 参数列表不同 (不同型 同型不同个 顺序)
- 返回值不同
递归 #
- 在调用过程中不断的调用自己
public class text5 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 1;
System.out.println(add(a));
}
static int add(int a){
return a==5?5:a+add(a+1);
}
}斐波那契 #
{% folding red, java %}
public class text7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请月份数:");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("第" + n + "个数:" + f(n));
// for (int n=1;n<50;n++){
// System.out.println("第"+n+"个数:" + f(n));
// }
}
public static long f(int n) {
return n==1 || n==2 ? 1 : f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}
}{% folding red, python %}
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
def f(n):
return n if n < 2 else f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
num = input('请输入:')
print(f(int(num)))进制转换 #
- 思路: 将输入数除2判断 商是否等于0 如果等于0则终止返回,不等于0 返回余数+方法*10 每次执行方法返回的值都要乘10 最后将每次计算的都加起来
//十进制准换二进制
import java.util.Scanner;
public class text9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入十进制数:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(toBin(num));
}
static int toBin(int num) {
return num == 0 ? 0 : num % 2 + toBin(num / 2) * 10;
}
}面向对象 #
- 封装 权限 访问接口
- 继承 原有的基础之上扩展性 兼容 单继承
- 多态 符合规则的继续大范围扩展 向上造型 向下造型
- 抽象
类和对象的概念 #
- 对象: 实际存在的事物
- 类: 实际存在的事物进行抽象形成的模板,描述对象的共同特征
对象的创建和使用 #
- 类定义之后,就有了模板 模板可以创建对象 了可以创建任意多个对象
- 创建类 new 构造方法()
- 如果想使用创建的对象 需要使用变量来承接
- 不赋值有默认值,主动赋值默认值消失
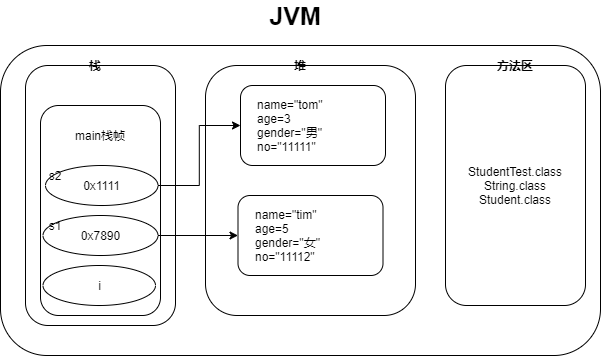
JVM内存管理 #
- 栈: 先进后出 (在程序运行的过程中存放局部变量和运行中的方法)线性地址连续
- 方法区:已被加载的类信息,常量,静态变量;
- 堆: 虚拟机启动的时候,创建堆;存放对象;地址可以不连续
- c语言中指针是操作存储空间 java不可以操作堆地址 只能使用堆中的信息,栈中引用是指是对象的地址;打印出来的不是地址,这个变量是基本类型局部变量
构造方法Constructor #
- 定义: 构造方法是类中一种特殊的方法,通过构造方法可以完成对象的创建,以及对象属性的初始化操作
- 修饰词 类名(参数列表){方法体}
构造方法没有返回值类型,构造方法的方法名和类名相同,构造方法同来创建对象,并且为对象初始化实例变量,一个类中可以定义多个构造方法,需要符合方法的重载,实质是有返回值,返回值类型是类,类中不写构造方法,默认系统会自动生成一个无参构造方法
作用 #
- 创建对象
- 初始化对象(方法中必须赋值)
public class text5 {
int year;
int month;
int day;
public text5(int y, int m, int d) {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
year = y;
month = m;
day = d; // 就近原则this
}
void show() {
System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
}
}
// 构造方法
public class text6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
// 创建日期对象
text5 d5 = new text5(2021,7,22);
d5.show();
System.out.print("------------");
}
}
方法的重載 #
构造方法也有方法的重载
空指针异常 #
- 引用为空
- 引用对象=> 空指针错误
java.lang.NullPointerException
package demo1;
public class text10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
text8 d = new text8(2000,10,2);
text9 t9 = new text9();
text8 w = new text8();
w.year = 1999;
w.month = 5;
w.day = 4;
t9.name = "张三";
t9.id = "001";
t9.birth = d;
Wife n = new Wife("李四","002",w);
System.out.println(n.birth.ShowDate());
System.out.println(t9.birth.ShowDate());
}
}
//
package demo1;
public class text8 {
int year;
int month;
int day;
public text8() {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}
text8(int y,int m, int d){
year=y;
month=m;
day=d;
// System.out.println(ShowDate());
}
String ShowDate(){
return year+"-"+month+"-"+day;
}
}
//
package demo1;
public class text9 {
String name;
String id;
text8 birth;
public text9() {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}
}
//
package demo1;
public class Wife {
String name;
String id;
text8 birth;
public Wife() {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}
public Wife(String string, String string2, text8 d) {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
name = string;
id = string2;
birth = d;
}
}
封装 #
在面向对象程式设计方法中,封装(英语:Encapsulation)是指一种将抽象性函式接口的实现细节部份包装、隐藏起来的方法
- 封装的优点
良好的封装能够减少耦合。
类内部的结构可以自由修改。
可以对成员变量进行更精确的控制。
隐藏信息,实现细节。
提供公共的入口 使用
set修改 和get访问 方法
public class Product {
private int pro_id;
private String pro_name;
private int pro_price;
public Product() {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}
// 设置
public void setId(int i) {
pro_id = i;
}
public void setName(String i) {
pro_name = i;
}
public void setPrice(int i) {
pro_price = i;
}
// 查看
public int getId() {
return pro_id;
}
public String getName() {
return pro_name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return pro_price;
}
// 有参封装
Product(int i,String n,int p){
pro_id = i;
pro_name = n;
pro_price = p;
}
// 返回所有的情况
String ShowProduct(){
return "商品id为:"+pro_id+"\n商品名称为:"+pro_name+"\n商品价格为"+pro_price;
}
}
// 调用
public class Build {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product p1 = new Product();
p1.setId(1);
p1.setName("手机");
p1.setPrice(12000);
Product p2 = new Product(2,"电脑",22222);
System.out.println(p2.ShowProduct());
System.out.println(p1.getPrice()); // 获取单个商品的信息 使用get方法
System.out.println(p2.ShowProduct());
}
}
this 关键字 #
- this本质是对象的地址,this关键字指向的是当前对象的引用
- this 内容相同 每个this指向对象的地址 都在堆中
- 本质就是一个变量或者引用,存储在对象的内部
- this本身的内容就是该对象的地址值
- this关键字来区分局部变量和实例变量。
- 在构造方法中 使用
this() = new 构造方法只能在构造方法中的第一行使用
